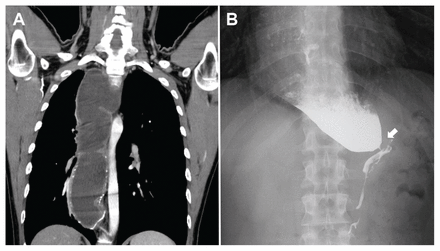
A 29-year-old man presented to the emergency department with worsening heartburn and regurgitation, despite taking proton pump inhibitors and antacids for several months. He had a 10-year history of dyspepsia with dysphagia of solid and liquid food. We obtained a chest radiograph (Appendix 1, available at www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230111/tab-related-content), which showed lateralization of the azygoesophageal recess with a right posterior mediastinal mass density. A computed tomography (CT) scan showed a markedly dilated esophagus with a thick, calcified wall (Figure 1A). An upright barium esophagram (Figure 1B) showed a dilated proximal esophagus with distal narrowing in a bird’s beak morphology (arrow). Suspecting achalasia or esophageal cancer causing pseudoachalasia, we arranged for the patient to undergo upper endoscopy, which showed no evidence of tumour and was consistent with achalasia. He underwent a peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). At 2-year follow-up, he was doing well, with good oral intake and an Eckhardt score (a clinical score for achalasia) that had improved from 12 to 1.
(A) Computed tomography scan of a 29-year-old man with achalasia, showing a markedly dilated esophagus with a thick, calcified wall. (B) An upright barium esophagram showed a bird’s beak morphology (arrow) that resulted from failure of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax during swallowing.
Achalasia is an esophageal motility disorder characterized by insufficient relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter and absence of peristalsis.1 It is uncommon and occurs equally in both genders and across all races.1 Mean age at diagnosis is older than 50 years but it can be seen in children and young adults.1 Presenting symptoms include progressive dysphagia for solids and liquids (90%), heartburn (75%), regurgitation of undigested food (45%) and respiratory complications, including nocturnal cough and aspiration (20%–40%).2 For patients with dysphagia who have intact oropharyngeal swallowing, mechanical obstruction should be excluded via either endoscopy or a CT scan, before assessing for abnormal motility with esophageal manometry.1,2 Treatment options for achalasia include injection with botulinum toxin, pneumatic dilation, laparoscopic Heller myotomy and, more recently, POEM; these relieve symptoms by reducing the hypertonic contraction of the lower esophageal sphincter, improving esophageal emptying. Choice of treatment should be based on the availability of local expertise, patient preferences, cost and patient suitability for the intervention.3
Footnotes
-
Competing interests: None declared.
-
This article has been peer reviewed.
-
The authors have obtained patient consent.
This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original publication is properly cited, the use is noncommercial (i.e., research or educational use), and no modifications or adaptations are made. See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
Achalasia with megaesophagus - CMAJ
Read More

No comments:
Post a Comment